Cosmetic Dentistry Procedures That Enhance Your Smile
Blog
Cosmetic Dentistry Procedures That Enhance Your Smile
Introduction:
We have compiled this article on “Cosmetic Dentistry Procedures That Enhance Your Smile.” The reference links are at the bottom of the article.
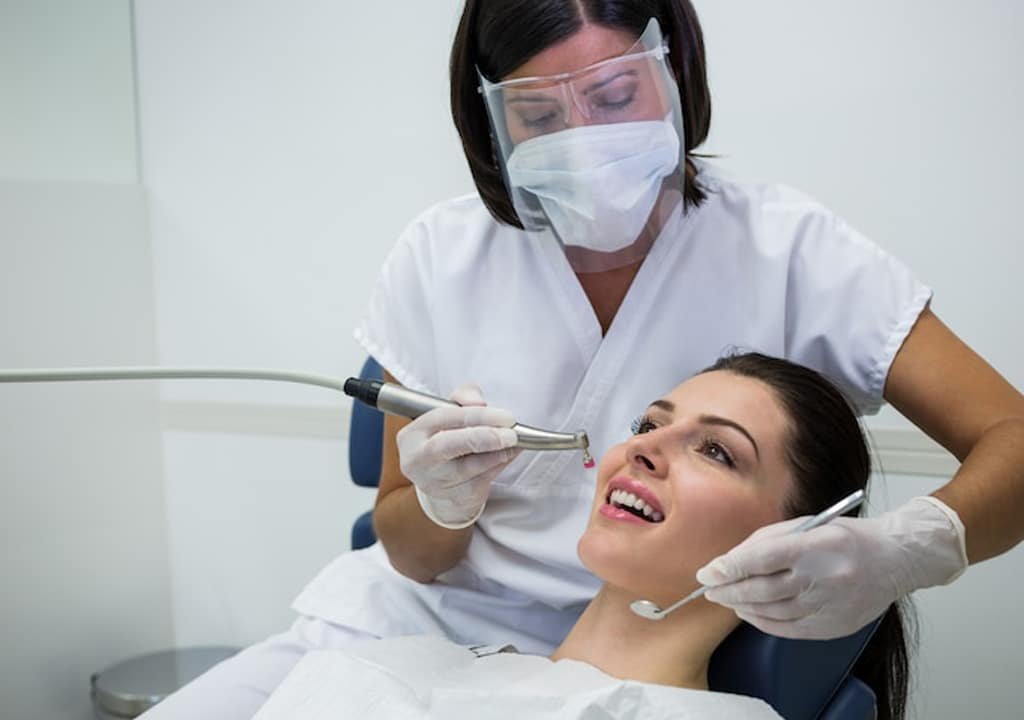
[1]Cosmetic dentistry is more popular than ever, from whitening and shaping to closing spaces and replacing teeth. And dentists have a large selection of tools and techniques for improving the look of your smile.
Before deciding to undergo any cosmetic procedure, it’s important to know the benefits and risks and what you can expect during the process. Make sure you’re clear about what it will cost, how much experience your dentist has with the procedure, and whether any special maintenance will be needed afterward.
Teeth Whitening
Over time, teeth can become stained or discolored, especially after smoking, taking certain medications, or consuming foods and beverages such as coffee and tea. Using a chemical process, your dentist can bleach your teeth in one of two ways. They can do an in-office procedure, or provide you with a system to use at home.
Your dentist can create a custom mouthpiece tray that ensures the right amount of whitening solution reaches your teeth. You may find whitening at home more convenient. But it can take 2 to 4 weeks or longer depending on the strength of peroxide used. In-office whitening can take place in one or more 1- to 2-hour visits.
Keep in mind, your teeth can become stained again if you continue exposing them to the same substances that originally stained them. Because whitening products are not meant to clean teeth, it is still important to continue practicing daily oral hygiene by brushing twice a day, flossing at least once a day, and rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash daily.
Bonding
Bonding may improve how your teeth look if they have excess space between them, or if they are chipped, broken, stained, or cracked.
Dentists also use bonding materials to fill small cavities or to protect the exposed root of a tooth.
The dentist can usually do this procedure in a single office visit by applying an etching solution followed by tooth-colored materials — sometimes composite resins — directly to the tooth’s surface where needed.
Although bonding can last for several years, it is more likely than other types of restorations to chip or become stained or just wear down.
[2]Before You Start Treatment
Before you start any cosmetic dental procedures, it is important to see a dentist to check your whole mouth thoroughly. This is to:
- Treat any disease first. Your health is the priority.
- Find out what is causing the unsatisfactory appearance of your teeth.
- Talk about the range of treatment options.
- Work out a realistic plan that suits you.
What Is Important To You?
Before You See Your Dentist, Think About:
- What you like and don’t like about the appearance of your teeth.
- Any symptoms you may have, such as pain or difficulty eating.
- Treatment you have had in the past and whether you were happy with it or not.
- What you would like to change. Bring a photo if it helps; for example, how your teeth used to look before they were chipped.
- How much time and money you would be prepared to invest. If you have private health insurance, check what sort of dental treatment is covered.
- How much effort you would be prepared to put into looking after your teeth at home in the future. Most cosmetic dental treatment requires extra care at home to prevent tooth decay, gum disease or other problems. Cleaning the area well and having a healthy diet is essential.
It may be useful to write your thoughts down.
Questions To Ask
During your appointment with the dentist, talk about your concerns, using the list above as a starting point. Your dentist may take some x-rays and do some other tests. Ask your dentist about:
- What options are available – the pros and the cons.
- What results can be reasonably expected.
- Costs – time and money, and payment options.
- Possible side effects or complications.
If it is a simple procedure, it may be done on the day. If it is a complex procedure, you may need to time to think about your options, or see specialists over multiple visits. Together, you and your dentist can come up with a plan that suits you.
Conclusion:
Thank you for reading this article, and check back frequently for other dental health articles. Should you have any questions, please contact Apple Tree Dental today!
Article compiled by Apple Tree Dental
Article reference links
Ignorance Of Dental Pain
Blog
Ignoring Dental Pain? Here’s Why You Shouldn’t
Introduction:
We have compiled this article on “Ignorance Of Dental Pain”. The reference links are at the bottom of the article.
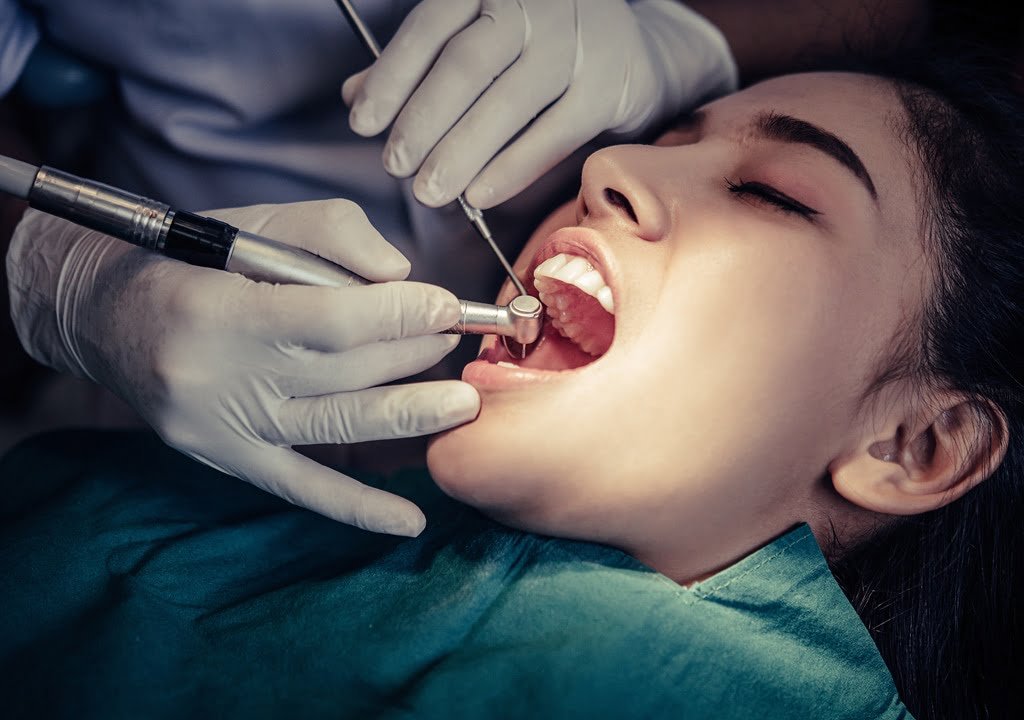
[1]Oral disorders such as dental caries and periodontal disease are worldwide public health problems. The “Global Burden of Oral Conditions in 1990–2010” report showed that oral conditions continue to be highly prevalent, affecting about 3.69 billion people. In this report, untreated dental caries in the permanent dentition was identified as the most common of all the evaluated disorders, having the highest worldwide disease load, affecting 35% of all age groups. Severe periodontitis was the sixth most prevalent condition (11% of world population) and untreated caries of the primary dentition was the tenth (9% of world population). Severe tooth loss was the 36th most prevalent condition, affecting 2% of the world’s population]. A number of studies from around the world state that 60–90% of schoolchildren suffer from dental caries.
In Latin America, dental caries is among the most frequent untreated health conditions among preschoolers, schoolchildren, and adolescents, who have limited access to restorative dental treatment. In Mexico, dental caries is the primary public oral health problem; for example, at 12 years of age between 70 and 85% of schoolchildren exhibit caries in the permanent dentition, with a high prevalence of untreated cases. Dental caries is also the main cause of dental death in various age groups, presenting a serious challenge to the oral healthcare system due to high care costs.
Oral and dental diseases can cause pain, suffering, functional deterioration, and diminished quality of life. The high cost of treatment constitutes a substantial burden to the national health system and for individual households. Families often opt to pay directly for dental care in an effort to maintain adequate oral health among household members. In developed countries, oral health treatment represents from 5 to 10% of health expenses. This treatment is unavailable or extremely limited in many developing countries, where affected teeth are often not treated or merely extracted, making them the main source of pain. For decision-makers in different countries, especially in the “developing” ones where the burden of disease is high, it is necessary to consider oral health as a priority and having recent epidemiological data is essential.
The experience of pain, considered a normal consequence of organ or system disorders, is a ubiquitous public health concern. Untreated dental caries generally leads to dental pain. Although dental pain can seriously affect peoples’ daily life, negatively affecting quality of life, few epidemiological studies on oral health include questions on dental pain. Orofacial pain, and especially dental pain, can cause sleep loss, diminished work effectiveness or academic performance, absence from school or work, weight loss, and avoidance of certain foods. Some researchers treat it as a predictor of dental health service use (usually curative or emergency). In this type of care, teeth receive nonregressive treatments that can predispose them to loss over time; it can also raise the probability of an edentulous old age.
General medical practitioners are often called upon to manage acute dental pain in emergency situations, for example, out of hours or in rural Australia, where it may not be possible for a dentist to provide immediate treatment. Common acute oral problems are usually easy to diagnose. Simple management can alleviate pain and further discomfort until a dentist can be called upon.
Most problems can be identified by the history and examination. Several dental conditions have typical symptoms with different types of pain.
[2]Which Tests Can Assist In Diagnosis?
There are several simple tests that may assist in diagnosis of dental pain.
Pulp Sensitivity Test
Dry ice, or an ordinary ice stick (made in a plastic or glass tube), is placed on the cervical third (neck region) of the tooth crown. A response to the stimulus indicates that the pulpal tissue is capable of transmitting nerve impulses. No response may indicate pulp necrosis.
Percussion Test
Using an instrument handle, the tooth is tapped in the longitudinal axis. A painful response suggests possible periapical inflammation.
Probing
Placing a fine, blunt probe gently into the gingival sulcus surrounding the tooth enables the health of the gingival tissues to be assessed. Bleeding and/or sulcus depths greater than 3-4 mm indicate gum disease.
Mobility Test
Holding a tooth firmly on the buccal (cheek) and lingual sides between the fingers enables mobility to be assessed. All teeth have a small amount of mobility (
Palpation
Careful palpation around the area of concern may reveal tenderness and the type and extent of swelling.
Radiographic Examination
If it is possible to obtain a screening radiograph, such as an orthopantomograph (OPG), this may assist in the diagnosis and localisation of the cause of the pain. The radiograph should show clearly the apical and periapical structures of teeth and associated tissues. The relationship of the maxillary molars and premolars to the floor of the maxillary sinus can be examined, and radiographs may reveal recurrent caries or periapical radiolucencies associated with an established infection
-
https://www.nps.org.au/australian-prescriber/articles/management-of-acute-dental-pain-a-practical-approach-for-primary-health-care-providers ↑
Conclusion:
Thank you for reading this article, and check back frequently for other dental health articles. Should you have any questions, please contact Apple Tree Dental today!
Article compiled by Apple Tree Dental
Wisdom Tooth Removal: What Happens When You Ignore Impacted Teeth For Long?
Blog
Wisdom Tooth Removal: What Happens When You Ignore Impacted Teeth For Long?
Introduction:
We have compiled this article on “Wisdom Tooth Removal: What Happens When You Ignore Impacted Teeth For Long?”. The reference links are at the bottom of the article.
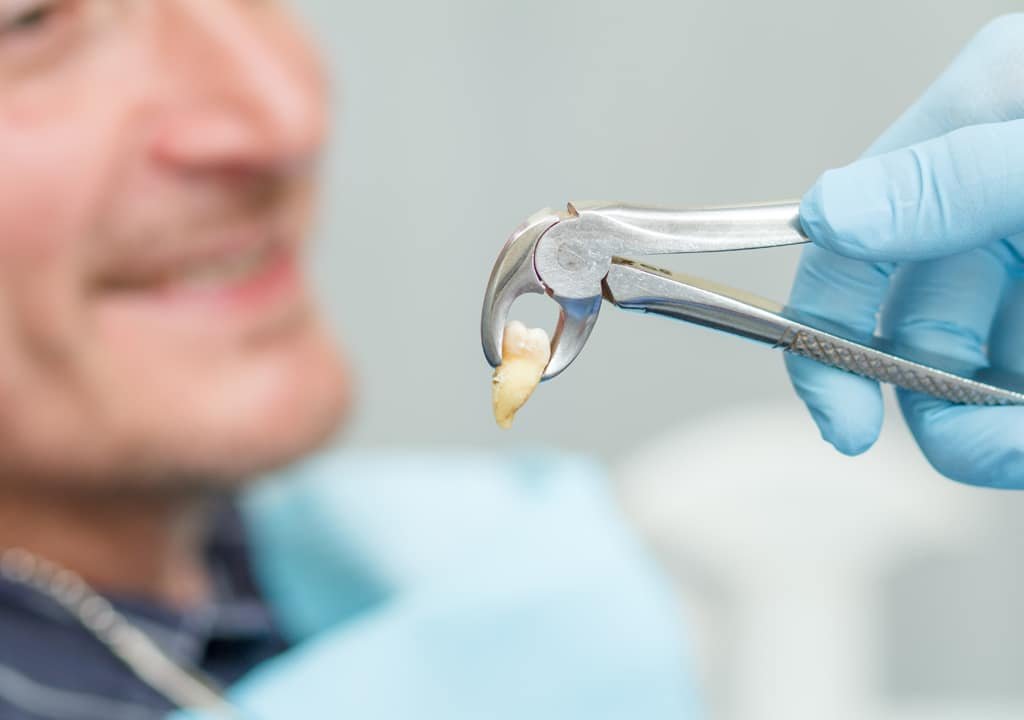
[1]Well, the unfortunate news is that 9 out of 10 people will have at least one impacted wisdom tooth requiring removal. With that in mind, let’s take a closer look at wisdom teeth – what are they exactly and what happens if you leave them untreated.
Wisdom Teeth 101
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the very last teeth in the jaw to develop, and are located in the back most part of your mouth. These teeth often appear during what has been called the “Age of Wisdom”; that time of life between the ages of 17 and 25 years old.
Looking back in our human history, wisdom teeth didn’t give us the hassles they do today. Our hunter-gatherer ancestors primarily ate a diet of raw vegetables and meat which required large, strong jaws to chew – their third row of molars were helpful! Then, with the emergence of agricultural farming practices, our diets changed significantly. Early farmers had a much softer diet of cooked foods that didn’t demand as much chewing strength. Our skull and jaw sizes responded to these dietary changes by getting smaller. But while our jaws got smaller, our teeth size and number did not similarly decrease. So now most of us are left with the unfortunate situation of having relatively small jaws that just don’t have the room needed to best accommodate our wisdom teeth.
When Can I Keep My Wisdom Teeth?
We’re not all built the same, and truthfully some jaws can still accommodate wisdom teeth just fine. In these relatively few cases, wisdom teeth can “erupt” (that is, come completely through the gum) without any pain, disease, or other dental problems. In these cases, your oral surgeons may not recommend immediate extraction, but rather will recommend strongly that you stick to regular check-ups and cleanings with your dentist, that you maintain excellent oral hygiene practices at home, and receive periodic x-rays to evaluate the ongoing health of your wisdom teeth.
When Do My Wisdom Teeth Need To Be Extracted?
When a wisdom tooth doesn’t fully erupt through the gums, it is called an ”impacted” tooth. An impacted tooth is one that is unable to fully enter into the mouth through the gums because there just isn’t enough room. An impacted tooth can cause a whole host of problems, including:
- Difficulty maintaining adequate brushing, which can lead to tooth decay and infection.
- Damage to neighboring teeth.
- Pain from pressure of the tooth overcrowding.
- Systematic infections and illnesses that can affect the heart, kidneys and other organs when oral bacteria travels from the mouth into the bloodstream.
- Fluid-filled cysts or tumors can form that can lead to hollowing of the jaw and damage to surrounding nerves.
[2]When Your Dentist Recommends Extraction
It’s imperative that you see a professional dentist for your impacted wisdom tooth. He or she can let you know when extraction would best be completed. You don’t want to wait to see a dentist when it comes to impacted wisdom teeth.
Impacted wisdom teeth are essentially trapped inside your jawbone. Leaving them alone could mean incurring jaw pain or even complications that would make extraction more difficult. If there are complications during your extraction, not only could the procedure be more expensive, your recovery time could take longer.
Signs to look out for with impacted wisdom teeth include pain, swelling, bleeding, or bad breath, which could mean you have an infection. Your dentist or oral surgeon can help you decide when the best time to extract your impacted wisdom tooth is.
Impacted Wisdom Teeth Can Ruin Orthodontic Work
Impacted wisdom teeth are more than just nuisances that you need to get out. They can cause some major problems if left alone, even if there’s only one of them. If you’ve had any previous orthodontic work done, impacted wisdom teeth can ruin it.
These wisdom teeth can push against your rows of teeth, making them crowd together and pushing them forward. Teeth can quickly become misaligned and you may even need a second set of braces after the removal if you wait too long.
-
https://tahoeoralsurgery.com/blog/2018/dear-doctor-what-happens-if-i-ignore-my-wisdom-teeth ↑
-
https://yourdentalhealthresource.com/how-long-can-i-ignore-my-impacted-wisdom-tooth/ ↑
Conclusion:
Thank you for reading this article, and check back frequently for other dental health articles. Should you have any questions, please contact Apple Tree Dental today!
Article compiled by Apple Tree Dental
Invisalign Braces: A Perfect Smile Makeover
Blog
Invisalign Braces: Your Path to a Perfect Smile
Introduction:
We have compiled this article on “Invisalign Braces: A Perfect Smile Makeover”. The reference links are at the bottom of the article.
[1]If you’re discontented with the shape of your grin you tend to hide your pearly whites. For teenagers and adults universally, few things are more annoying than being told to “say cheese” for a photo. To put it in simple words, you are upset over crooked, misaligned teeth. Even though a lot of us have the choice of getting fitted for braces, many people directly find themselves picturing metal wired over teeth and abruptly feel that developing that perfect smile might not be for them in any case.
Opportunely, dental treatment technology has advanced a great deal in the past decades. This is since metal braces were the only choice for crooked teeth and wide gaps. Generally, you need to spend months or at times even years wearing conventional braces to unbend your smiles. However, clear braces have now become a very reasonably priced and easily available alternative. Actually, of late more men and women are gradually turning to Invisalign as their teeth alignment solution.
By now you must be wondering to know what is Invisalign?
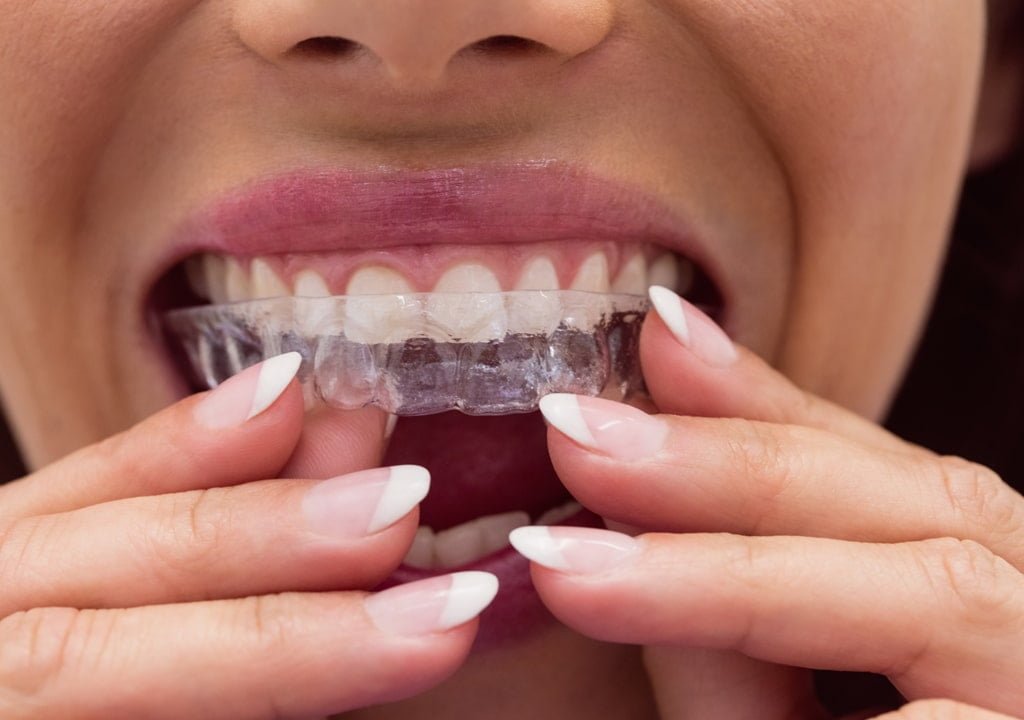
Invisalign: What Is It?
Invisalign, to put it in simple words, is one of the most accepted, remarkable solutions for uneven smiles and teeth-straightening. The clear braces available for teenagers and adults are designed to abolish spacing issues and teeth crowding simultaneously being almost invisible to the bare eye. This extremely admired progression in dentistry enables active men and women to get the smile they always wanted without the look and feel of conventional metallic braces.
Besides being transparent enough to be nearly invisible, Invisalign clear aligners also offer wearers a few benefits over usual braces. Suitable in its design, it is custom-made to fit match the wearer’s teeth. Most importantly, it is detachable for both brushing and eating. Generally, patients who use these aligners do not have to face any of the obnoxious fitting or uneasiness that happens with traditional braces. With no wires to be troubled about, the Invisalign wearers are capable to go about their everyday lives hardly noticing they’re wearing an aligner whatsoever. Certainly, people find that living with these aligners is both relaxing and easy.
These innovative aligners are admired not just for their user-friendliness but because they offer outstanding results. At times, quicker than metal braces. This is because this technology allows dentists who measure and fit their patients for the aligners to effortlessly check teeth movement as smiles progressively set straight. This means that you’ve made to order Invisalign is fitted to persistently give the required pressure to softly shift teeth into their usual, wished-for placement.
[2]How Can A Smile Makeover Change Your Life?
There are so many advantages and benefits of having perfectly straight teeth that you will definitely consider a smile makeover. Here are a few of them:
Boost’s self-confidence
It is true when they say your smile can impact your self-esteem and self-confidence. Crooked teeth tend to stain more easily and can lower a person’s confidence to smile freely. A smile makeover removes flaws from the teeth and gives you straight teeth that give you the confidence to put yourself out there.
Psychological & Physiological changes
When you smile your body releases three different hormones: dopamine, endorphins, and serotonin. These are responsible for making us feel happy, and they also help lower stress levels. In fact, when you smile more often, you attract people more. They make you a more appealing and attractive person to be around. This in turn will have a positive effect on your well-being.
Better oral health
In case of malocclusions like underbites, overbites, crowding, etc., there is a huge chance of more dental issues cropping up due to poor oral health. In this case, a smile makeover not only repositions your teeth to give you gorgeous straight teeth but also helps you build better oral health.
Smile Makeover With Clear Teeth Aligners
There are a lot of dental appliances that already exist on the market. However, with the advancement in technology, the dental world also caught up and took leaps and bounds to make the journey to get straight teeth a fairly comfortable process for the patients. For this, they took the help of 3D technology. Clear Teeth Aligners are transparent/clear/invisible plastic trays that are made to fit your teeth.
How Are Clear Teeth Aligners Better Than Other Options To Get A Smile Makeover?
A common question that comes up when considering orthodontic treatment for a smile makeover is whether clear teeth aligners are better than other dental appliances. If you’re exploring options with an Orthodontist in London Ontario, you’ll likely find that clear aligners are a popular choice due to their discreet appearance and convenience.
The answer is yes, in a lot of cases. Even though all the appliances have the same goal- to give you straight teeth, there are some significant advantages clear aligners have over other dental appliances. So how are they better?
- Aesthetically Pleasant: While most dental appliances look unpleasant to the eye, Clear Aligners are barely noticeable which is a major reason for their popularity. It is discreet enough to remain undiscovered which gives the patients the confidence of smiling even while receiving the treatment.
- Removable: Giving a big sigh of relief to most patients is the removable nature of the clear aligners. A lot of patients have suffered an insufferable amount of discomfort and pain during their journey to straight teeth. However, with clear aligners, one can remove the aligners and wear them again very easily and comfortably. But, word of advice, do not remove your clear aligners too frequently. Orthodontists recommend that aligners should be worn at least 20 – 22 hours a day for impactful treatment.
- Easy Cleaning: Everyone who has ever used braces or expanders knows they are a nightmare when it comes to maintaining oral hygiene. However, with clear teeth aligners, you will not face such an issue ever. This is also due to the fact that they can be removed and easy to clean.
- No Lifestyle Restrictions: As clear teeth aligners are easily removable, you can practically eat and drink, and do whatever you want without altering anything in your current lifestyle.
- Fewer Clinic Visits: Clear teeth aligners do not require tightening appointments, adjustments, or repairs as frequently as in the case of braces, so there are lesser clinic visits.
-
https://smilemakeoverofla.com/blog/invisalign-perfect-fit-your-smile/ ↑
-
https://flashaligners.in/blog/smile-makeover-with-clear-aligners-smile-makeover-with-clear-aligners/ ↑
Conclusion:
Thank you for reading this article, and check back frequently for other dental health articles. Should you have any questions, please contact Apple Tree Dental today!
Article compiled by Apple Tree Dental
Fix Your Smile With Best Smile Correction Treatment
Blog
Fix Your Smile With Best Smile Correction Treatment
Introduction:
We have compiled this article on “Fix Your Smile With Best Smile Correction Treatment”. The reference links are at the bottom of the article.
[2]Ways To Improve Your Smile
Keep Your Natural Sheen
Your smile is one of the first things that people notice about you. A healthy smile isn’t always achieved overnight, but takes a variety of methods to help create and maintain. Here are 10 easy things you can do to help improve the appearance and health of your teeth.
Floss Daily
Flossing removes plaque between teeth and out from under the gumlines, where a toothbrush can’t reach. Daily flossing helps prevent tooth decay and gingivitis. When left alone, plaque and tartar build up under the surface of the gumlines. This can cause periodontal disease, which leads to bone destruction and tooth loss.
To floss properly, wrap the floss tightly around your finger and insert in the space between your teeth. Gently slide it up and down under the gumlines two to three times. If bleeding occurs, this is most likely due to gingivitis or gum disease. When flossing daily, the bleeding associated with mild to moderate gingivitis usually stops after about two weeks.
If you just can’t stand flossing, try an oral irrigator. This device sprays water or mouthwash to remove plaque and food between your teeth and below your gumline.
See Your Hygienist Twice A Year
Having routine cleanings every six months helps to promote good oral health and a beautiful smile. When your cleanings are irregular, you can develop periodontal disease. This can cause unsightly swollen, receding, and bleeding gums. It’s also linked to health conditions like heart attack, stroke, diabetes, obesity, premature births, and sleep apnea.
In addition to removing stain and tartar from your teeth, your dental hygienist will also screen for health conditions like high blood pressure and oral cancer. Because many health conditions manifest themselves in the mouth, your dentist and hygienist can make you aware of issues that you should follow up on with your doctor.
Give Up Smoking
Smoking causes staining to your teeth. The stain from smoke is sometimes a superficial stain that can be polished off, but it can also soak deep into the enamel.
Smoking also damages healthy gums, causing them to recede and develop large pockets around the teeth. This makes teeth appear longer and creates dark spaces between them. Smoking also makes it very difficult to reverse gum disease.
Limit Your Coffee, Tea, And Red Wine
Drinks like coffee, tea, and red wine are known for staining teeth. Similar to smoking, these drinks can build up a superficial stain that your dentist or hygienist can polish off. But they can also cause internal staining of your tooth enamel.
Drinking through a straw can help reduce the stain on your teeth and may help reduce the risk of tooth decay. It can also help to rinse your mouth frequently with water so the dark liquid does not sit on your teeth for a long period between meals.
Choose Your Whitening Products Carefully
Depending on your needs, there are a variety of whitening products available: gel pens, rinses, toothpastes, strips, over-the-counter trays, custom trays, and laser whitening. While the choices can be overwhelming, each type can have specific benefits that help you target problem areas. Whitening toothpastes and rinses are good for coffee and tea drinkers. Gel pens are good for touching up small areas, like a tooth that has shifted back and collects more stain. Custom trays and laser whitening provide professional strength whitening and offer the most dramatic results.
Buy A Quality Toothbrush
Top quality electric toothbrushes are clinically shownTrusted Source to remove more plaque and achieve healthier gums than standard manual toothbrushes. Many now feature modes for whitening and sensitive teeth. The toothbrush bodies are made to last for years, while the heads can be changed out routinely as they age, or for sharing among family members.
If you’re not ready to shell out the dough for an electric toothbrush, be sure to purchase a soft bristled manual brush. While medium and hard bristled brushes are readily available on the market, dental professionals adamantly advise against their use. Stiffer bristles and aggressive brushing causes gums to recede and can wear enamel away from the teeth.
Drink Plenty Of Water
Water is the healthiest drink for your smile and your body. It helps flush teeth clean and discourages tooth decay. Tap water is the best choice as it has the recommended dosage of fluoride. Many times bottled water comes from a source where the fluoride levels are not monitored, or contain no fluoride at all. A healthy level of fluoride promotes tooth health and discourages decay.
Frequent consumption of acidic or sugary drinks can increase decay rates dramatically. Athletes are quickly becoming an at-risk group as the effects of sports drinks take a toll on their teeth.
Improve Your Other Health Conditions
Conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and bruxism (also known as teeth grinding) can all affect the health and appearance of your smile. When the body is strained by one health condition, it’s more difficult to treat another.
Rather than covering up symptoms, you can help improve your health through preventive methods. Eating right and getting enough exercise can dramatically improve the appearance of your body, teeth, and gums.
Get Dental Treatment In A Timely Manner
Dental conditions never correct themselves on their own. Tooth decay left untreated can easily transform a small cavity into a large tooth abscess. Where a tiny filling may have been all that was needed, it may now require a root canal and a crown.
Treating your tooth decay early means you’ll need smaller and less invasive dental restorations. This helps maintain the structure and stability of the tooth and keeps treatment costs lower. If left untreated, decay can spread to other teeth and may cause infections throughout the rest of your body.
Brush Your Teeth Twice A Day
This is a given, but many people still need to be reminded to brush their teeth at least twice a day. Because plaque can harden into tartar, frequent brushing helps teeth to stay whiter and healthier than in people who brush less often.
How you brush is also important. Angle the bristles toward the gumline at a 45-degree angle, with just enough pressure to make the tissue a lighter color. Gently make small strokes, focusing on only one or two teeth at a time. This will keep your gums healthy and remove the most plaque.
Form Good Habits For A Great Smile
It can take some time before you start to notice changes from whitening or improved oral hygiene. While these changes don’t come overnight, they are certainly worth the time and effort, both for the sake of your smile and your overall health.
-
https://dentalexpress.in/blogs/news/fix-your-smile-with-best-smile-correction-treatment#site-main ↑
-
https://www.healthline.com/health/improve-smile#brush-twice-a-day ↑
Conclusion:
Thank you for reading this article, and check back frequently for other dental health articles. Should you have any questions, please contact Apple Tree Dental today!
Article compiled by Apple Tree Dental