If you’re researching orthodontic treatment in London, Ontario, you’re likely asking: is Invisalign faster than braces?
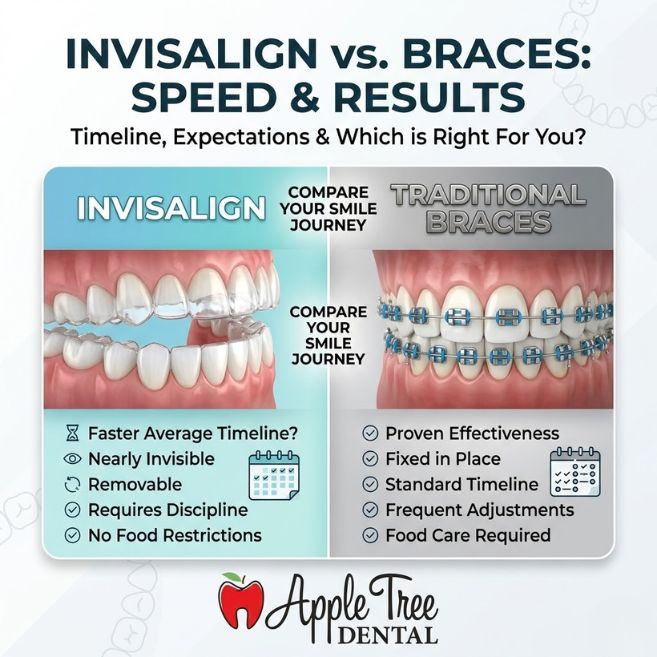
Is Invisalign faster than braces? In mild to moderate cases, Invisalign often completes treatment in 6 to 18 months. However, for complex bite corrections, traditional braces may provide more precise control and similar timelines depending on individual needs.
Choosing between braces vs aligners is not just about speed. It’s about case complexity, lifestyle, cost, and long-term results. This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know — backed by orthodontic principles recognized by organizations like the American Dental Association, Health Canada, and the Canadian Dental Association.
Invisalign vs Braces: How Each Treatment Works
Understanding how teeth move helps answer whether Invisalign dental braces work faster than traditional braces.
Invisalign (Clear Aligners)
Invisalign uses custom-made, removable plastic aligners designed through digital 3D scans. Each aligner applies gentle, controlled pressure to gradually shift teeth into position. Patients switch trays every 1–2 weeks.
Because treatment is digitally mapped from start to finish, movement is pre-planned and sequential.
Traditional Braces
Braces use brackets bonded to teeth, connected by archwires that are adjusted periodically. They provide continuous force and are especially effective for complex tooth movements.
Both systems rely on biological bone remodeling — a process that takes time regardless of the method used.
Is Invisalign Faster Than Braces? A Timeline Comparison
Average Treatment Duration
| Condition Severity | Invisalign | Braces |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Alignment | 6–12 months | 12–18 months |
| Moderate Issues | 12–18 months | 18–24 months |
| Complex Cases | 18–24 months | 24+ months |
In many mild cases, Invisalign may finish several months sooner than braces. But in advanced cases, braces may offer more predictable outcomes.
So, are Invisalign faster than braces?
Often yes — but only when the case is suitable.
What Determines Treatment Speed?
The timeline depends less on the brand and more on biological and mechanical factors.
1. Complexity of Tooth Movement
Severe crowding, large gaps, or bite correction may require fixed braces for maximum control.
2. Patient Compliance
Invisalign must be worn 20–22 hours per day. Removing aligners too frequently delays progress. Braces work 24/7 since they are fixed.
3. Age and Bone Density
Younger patients typically experience faster tooth movement due to more responsive bone structures.
4. Treatment Planning Technology
Digital mapping improves predictability in aligner therapy. However, biological limits still apply.
Orthodontic principles recognized by the American Dental Association emphasize that safe tooth movement requires controlled, gradual pressure regardless of the system used.
Invisalign vs Braces Cost in London, Ontario
Cost is another important factor when comparing invisalign vs braces.
Average Cost Range
- Invisalign: $4,000 – $8,000
- Braces: $3,500 – $7,500
The final invisalign vs braces cost depends on:
- Treatment complexity
- Length of treatment
- Additional appliances
- Retainers after completion
While Invisalign may sometimes cost slightly more, many patients prefer its discreet appearance and removability.
Clinics such as Apple Tree Dental in London, Ontario provide personalized orthodontic consultations to determine accurate timelines and cost estimates based on individual needs.
Braces vs Aligners: Effectiveness and Results
Both treatments can correct:
- Crooked teeth
- Gaps
- Overbite
- Underbite
- Crossbite
- Mild jaw misalignment
When Invisalign Works Best
- Mild to moderate crowding
- Cosmetic alignment improvements
- Adults seeking nearly invisible treatment
- Patients committed to wearing aligners consistently
When Braces May Be More Effective
- Severe rotations
- Complex bite correction
- Significant vertical movement
- Cases requiring strong anchorage
The Canadian Dental Association highlights that the success of orthodontic treatment depends on proper diagnosis and supervision, not just the appliance chosen.
Are Invisalign Faster Than Braces for Adults?
Adult orthodontic cases are increasingly common in London, Ontario.
For adults with minor spacing or alignment issues, Invisalign often completes treatment within 12–18 months.
However, adult bone density can slow movement compared to teens. In severe adult bite corrections, braces may provide more stable force control.
Health Canada regulates dental devices to ensure safety and effectiveness, reinforcing that both systems are clinically approved options when administered by qualified professionals.
Comfort and Lifestyle Considerations
Speed matters — but so does daily comfort.
Invisalign Advantages
- Nearly invisible
- Removable for meals
- Easier brushing and flossing
- Fewer emergency visits
Braces Advantages
- No need to remember wear time
- Continuous force
- Often better for complex alignment
For professionals, students, and families in London, Ontario, lifestyle flexibility often makes Invisalign appealing.
What to Expect During Treatment
Invisalign Journey
- Digital scan
- Customized aligner series
- Checkups every 6–8 weeks
- Gradual tray progression
Mild pressure is common when switching aligners, but discomfort is typically manageable.
Braces Journey
- Bracket bonding appointment
- Wire adjustments every 4–6 weeks
- Occasional soreness after tightening
Both require retainers after completion to prevent relapse.
Does Invisalign Always Finish Faster?
No.
Even if Invisalign appears faster in advertisements, orthodontic treatment depends on biological response and case complexity.
For example:
- Severe overbites may respond better to braces
- Rotated teeth sometimes require fixed brackets
- Compliance issues can extend aligner treatment
The key takeaway: Invisalign can be faster — but only in appropriate cases.
Choosing the Right Treatment in London, Ontario
When deciding between braces vs aligners, consider:
- Alignment severity
- Budget
- Lifestyle preferences
- Commitment level
- Desired aesthetics
At Apple Tree Dental in London, Ontario, treatment planning typically involves digital scans, bite analysis, and a customized timeline projection before recommending either option.
Final Verdict: Is Invisalign Faster Than Braces?
In many mild to moderate cases, Invisalign may complete treatment faster — often within 6 to 18 months. However, braces remain highly effective for complex corrections and may deliver better control in certain situations.
Instead of focusing only on speed, prioritize:
- Long-term stability
- Bite function
- Overall oral health
Consulting a dental professional ensures the right choice for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Invisalign faster than braces for mild cases?
Yes, Invisalign often completes mild alignment corrections within 6–12 months.
2. Are Invisalign faster than braces for severe crowding?
Not always. Braces may provide better control for complex movement.
3. Is Invisalign more expensive than braces?
Invisalign vs braces cost varies, but pricing overlaps significantly depending on case complexity.
4. Do aligners move teeth differently than braces?
Both use controlled pressure to shift teeth through bone remodeling.
5. Which option is better for adults?
For mild cosmetic concerns, Invisalign is often preferred. Severe cases may benefit from braces.
6. How can I know which is right for me?
A professional orthodontic consultation with digital imaging provides the most accurate answer.
Conclusion: Is Invisalign Faster Than Braces?
So, is Invisalign faster than braces? In many mild to moderate cases, yes — Invisalign can complete treatment within 6 to 18 months, often sooner than traditional braces. However, when it comes to complex bite corrections, severe crowding, or significant tooth rotation, braces may provide more precise control and equally efficient long-term results.
The truth is that treatment speed depends on:
- Case complexity
- Patient compliance (especially with aligners)
- Age and bone response
- Proper orthodontic planning
Both Invisalign dental braces and traditional braces are clinically proven systems supported by professional dental organizations such as the American Dental Association, Health Canada, and the Canadian Dental Association. When administered by qualified dental professionals, both options are safe and effective.